


This is a vector -valued second order linear differential equation. Find the velocity v(t) of a projectile thrown upward at time t 0 with speed v 0. All the basic kinematic equation youve learned come from one basic equation, d2x dt2 g d 2 x d t 2 g.
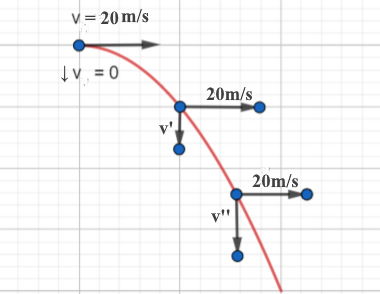
1 Motion in One Dimension Example 1 When a projectile moves slowly through air, the drag is linear in the velocity, F mv. For fun, see chapters I-1 through I-8 of the Feynman lectures. Hints And Numerical Answers For Projectile Motion Problems. kinematics, see chapter 1 of Kleppner and Kolenkow. Using our projectile motion calculator will surely save you a lot of time. kinematic equations to solve problems involving the one-dimensional motion of. Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y = h + V y 0 t − g t 2 / 2 y = h + V_\mathrm / (2 g) h max = h + V y0 2 / ( 2 g ).Horizontal distance traveled can be expressed as x = V x t x = V_\mathrm x t x = V x t where t t t is the time.
#Kinematics projectile motion problems and solutions free#
We tackled both problems in the horizontal projectile motion calculator and free fall calculator, respectively. If, additionally, α = 90°, then it's the case of free fall. (b) The net force acting upon the object causing this acceleration. MOTION AND ENERGY PROJECTILE MOTION Worksheet 1 : Review of Physics. (a) The magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the object. solving quadratic simultaneous equations solutions of non homogeneous equations. If the vertical velocity component is equal to 0, then it's the case of horizontal projectile motion. Problem (1): A 5-kg object moves around a circular track with a radius of 18 cm at a constant speed of 6 m/s. Three vectors - V V V, V x V_\mathrm x V x and V y V_\mathrm y V y - form a right triangle.The vertical velocity component V y V_\mathrm y V y is equal to V sin α V \sin\alpha V sin α.The horizontal velocity component V x V_\mathrm x V x is equal to V cos α V \cos\alpha V cos α.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
